
What is Bloodletting and what is Wet Cupping (Al-Hijama)?
Many confuse Hijama Wet Cupping therapy with Bloodletting. One technique is regarded as safe by science and the other is too invasive. We have made a research about the subject and puslished it below for educational purposes.
What is Bloodletting technique?
The practice of bloodletting was recorded as far back as 3,000 years ago, first by the Ancient Egyptians, then the Greeks and Romans, through the Middle Ages, and on to the Renaissance.
Bloodletting was the name given to the removal of blood for medical treatment. It was believed to rid the body of impure fluids to cure a host of conditions. Originally, bloodletting involved cutting a vein or artery; typically at the elbow or knee to remove the affected blood.
Over time, specialized instruments, and techniques including the use of leeches were developed to make more precise cuts and improve control over how much blood was removed. Blood was typically drained until you passed out, which for most people amounted to about 20 ounces of blood.
This technique would be considered as an invasive technique because it goes beyond the first layer of the skin which is the epidermis.
In the 21st century, this technique is still used for:
- Diagnostic purposes, to collect blood or serous fluids for medical reasons, or to donate blood for transfusion to others.
- Hemochromatosis is a genetic disorder that affects how the body processes iron. Today, this condition is treated with periodic blood draws to keep ferritin the protein that stores iron at a healthy level.
- Polycythemia vera is a stem cell bone marrow condition, blood may be drawn through phlebotomy to decrease the concentration of red blood cells and prevent clotting.
- Porphyria cutanea tarda causes inefficiency in how the body uses iron, resulting in dangerous iron accumulations. Iron levels may be kept in check with phlebotomy.
What is Wet Cupping Technique (Shartat Mihjam)
Wet Cupping (Shartat Mihjam)
Many people get confused between bloodletting and wet cupping, but there is a clear difference between those two techniques. The people use to interchange the name because of the basis that blood is drawn outside of the body, however, wet cupping technique is far from the bloodletting technique.
Wet Cupping skin scarification Shartat Mihjam consists of making shallow small and short superficial skin incisions. The length is around 1-2mm and depth is around 0.1mm. The blood is drawn out through capillary blood filtration by placing a suction cup on top of the skin. Skin scarification causes a minor bleeding and loss of blood cells through the induced superficial skin incisions. This technique is regarded as safe internationally because it doesn’t go beyond the skin epidermis. This technique is published in PubMed, Clinical Trials Gov, National Library of Medicine and in European Journal of Medicine and Natural Sciences.
The skin epidermis varies from 0.5mm for the eyelid to 4 - 5mm for the upper back. This is why this technique is considered non-invasive internationally. However, this technique must be done by a trained therapist with high hygiene standard and new materials.
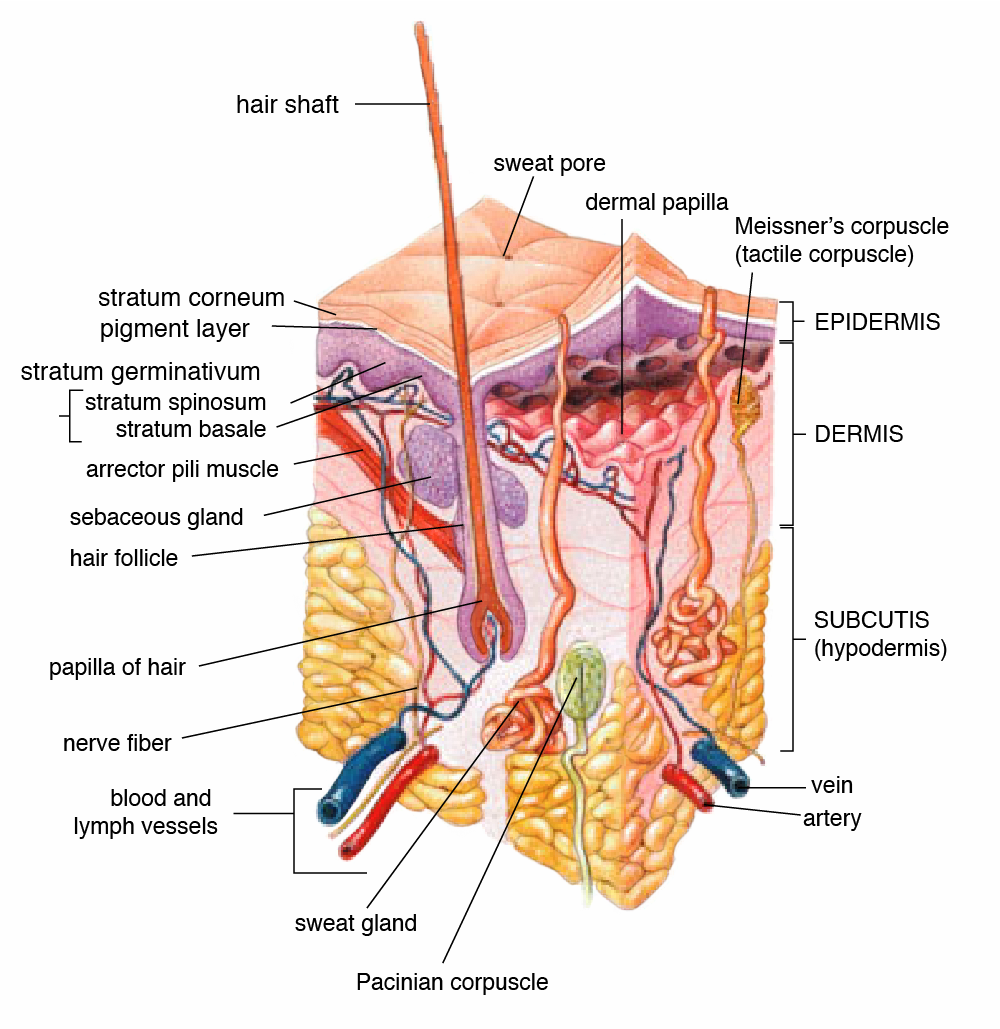
This figure of Anatomy of the Skin publish in Wikepedia shows the different layers of the skin; epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. A Certified Wet Cupping Practitioner will only make the scarification within the epidermis which is considered the safe zone. For example, people who need to test their glucose level also uses their lancet within the epidermis to draw out a small amount of blood.
Tattoo is more profond compared to wet cupping. The target of the tattoo artist is the top of the dermis layer (if the ink is on the top of the dermis, the ink will not leave the skin).
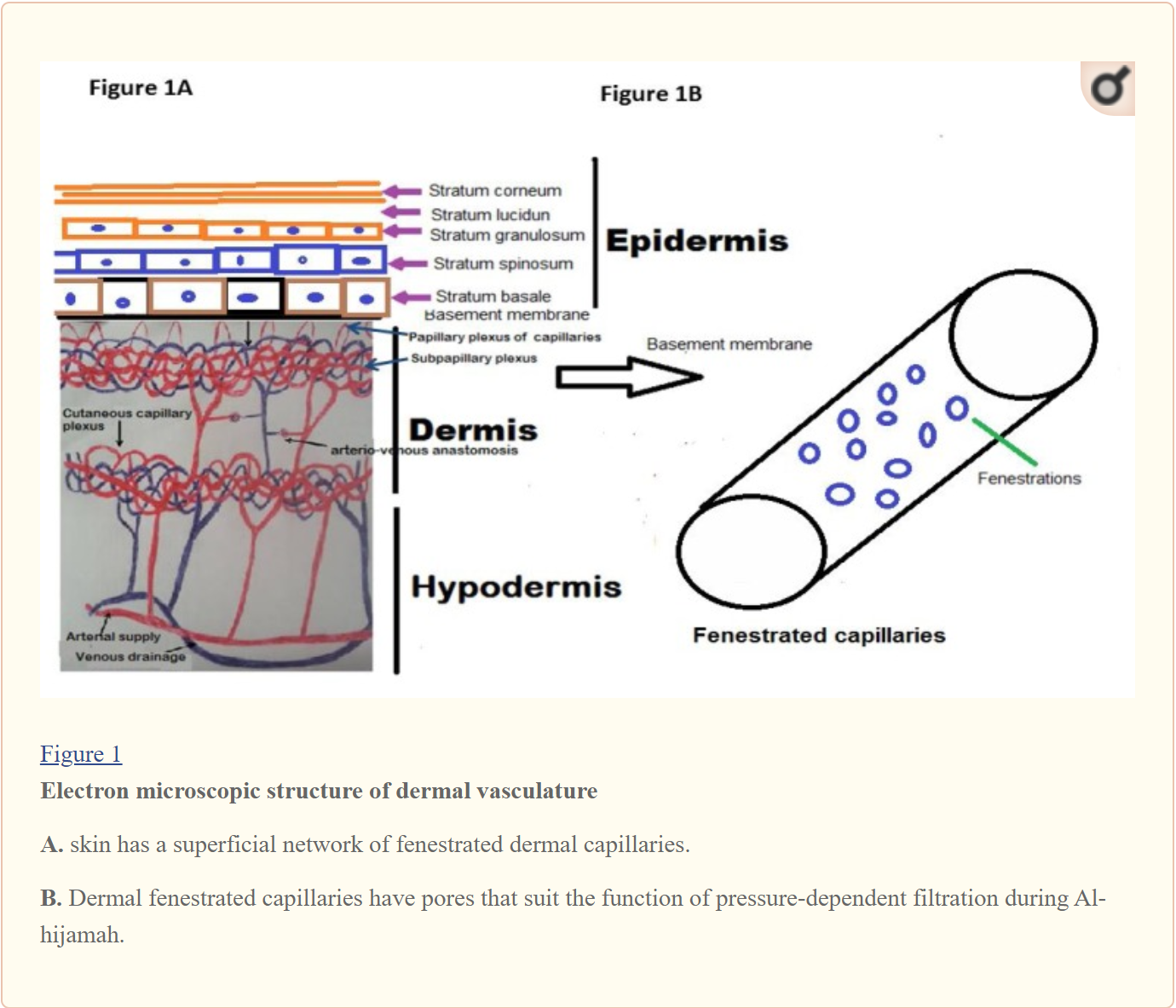
What is characteristic of the blood extracted in Wet Cupping?
Many international medical doctors have analyzed the blood that is extracted inside the cups and have concluded that the fluid that is filtrated by the percutaneous capillary blood filtration has causative pathological substances (CPS). The CPS are disease causing substance and disease related substance. They are present in the blood and in the interstitial fluid and they cannot be excreted by physiological mechanism.
Therefore, Wet Cupping therapy removes CPS from the site of pathology (whether the pathology is localized or generalized), from blood and from interstitial fluids. This enables pharmacological treatments to do better against a lower concentration of CPS, which prepares the site of pathology for a better response to administered pharmacological therapeutics. This may give a better chance for the immune system and homeostatic mechanisms to do better.
The figure above shows the percutaneous capillary in the skin.
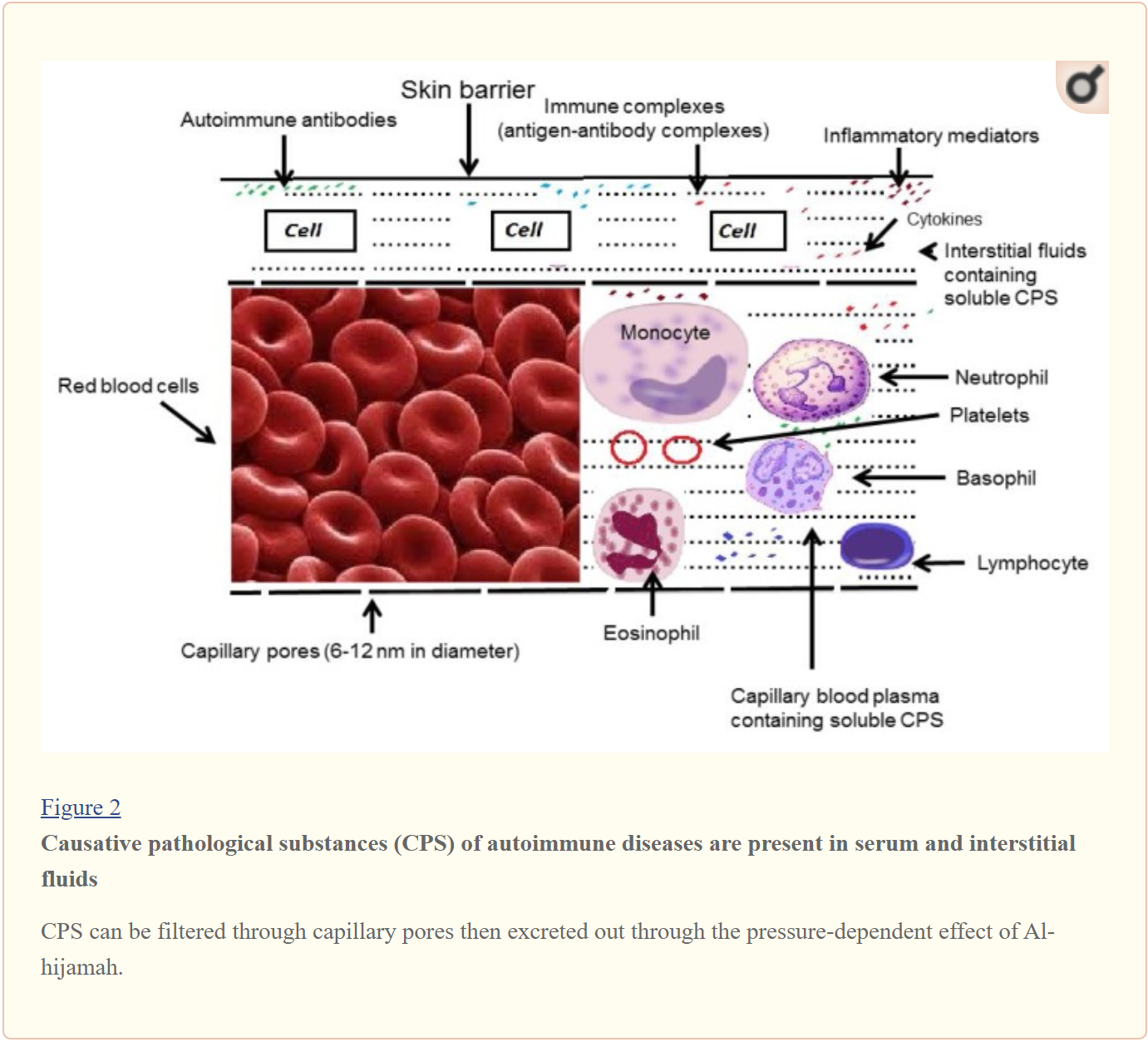
What are the so-called toxins (i.e. causative pathological substances; CPS)?
Based on the figure above, you can find inside the interstitial fluids and capillary blood plasma:
- Autoimmune antibodies
- Immune complexes
- Inflammatory mediators
- Cytokines
- Etc..
Wet Cupping will label these molecules as toxins if there are unwanted in the body and causes issues. For example, inflammation is a mechanism that is needed to protect our body from many harms. However, if someone has unwanted inflammation in a specific area for a long period of time this could lead to having health issues like arthritis.
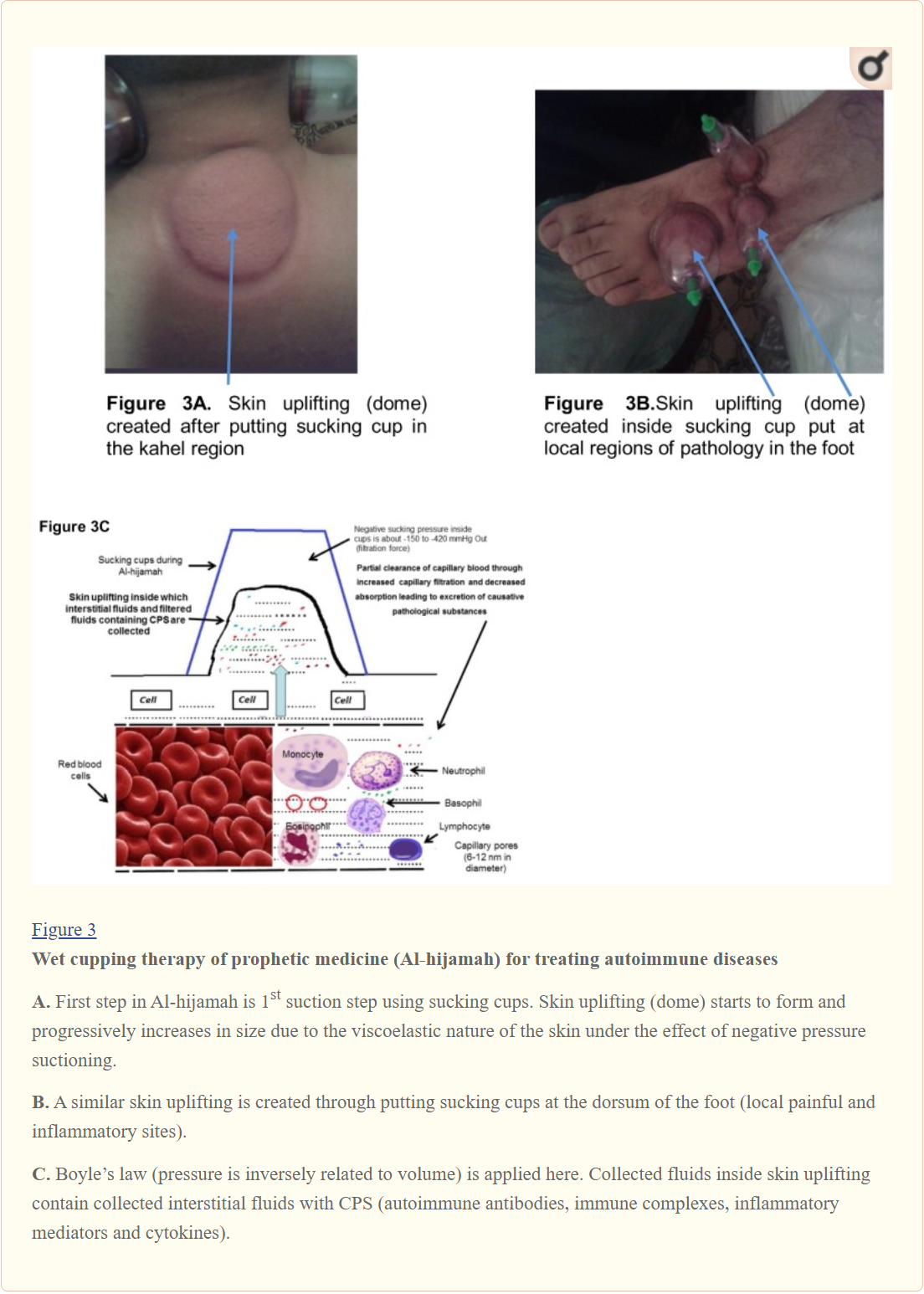
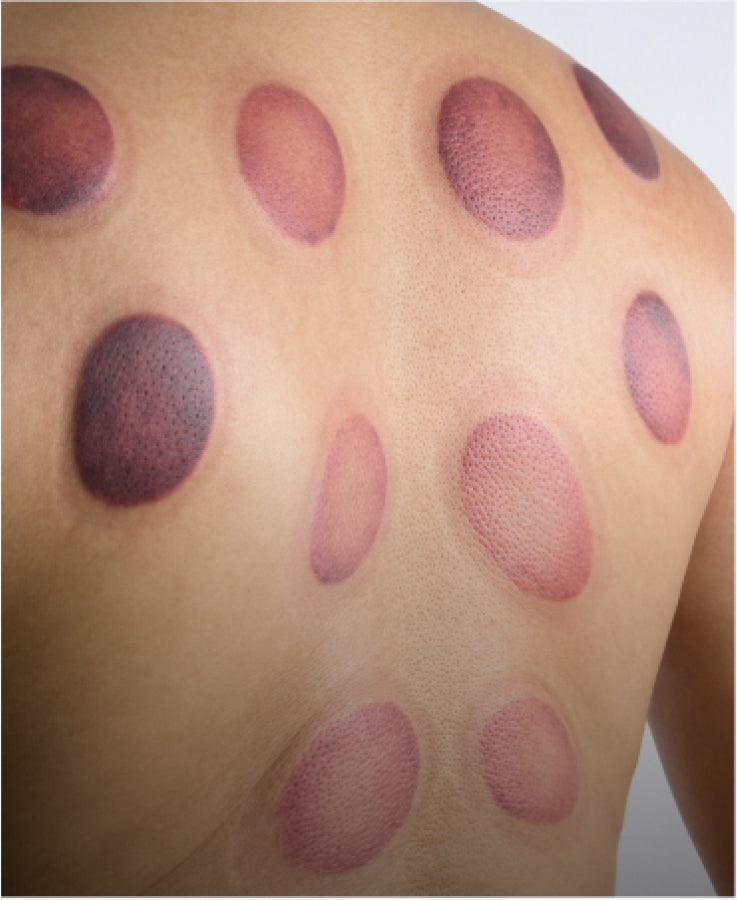
What happens when the skin is pulled by a vacuum cup; Dry Cupping?
Dry Cupping
When we apply a suction on the skin, the molecules can move towards the surface of the skin by filtration because of the pores. The Boyle’s Law is applied. Many athletes use this technique for recovery. This technique relaxes the muscles and it can be used for lymphatic drainage.
In traditional medicine, the result of the skin color after
applying dry cupping indicates the level of stagnation of the blood and amount of toxins (unwanted wasted).
- Dark purple-black marks: Lack of blood, heavy stagnation
- Purple with small dark spots within the cupping mark:
“Cold” Blood stasis, overconsumption of cold food. - Consistent purple spots: Blood stasis due to agitation and hot temperament
- Bright red: Yin-deficiency, lack of moisture.
- Dark red: High blood cholesterol, pathogenic heat
(“heat evils”)
Why is Wet Cupping more beneficial compared to Dry cupping?
Like mentioned above dry cupping pulls the molecules at the surface of the skin. However, not every unwanted toxins is cleared by doing dry cupping. In the case of heavy stagnation, it takes a lot of dry cupping sessions to force the lymphatic system to clean everything.
However, Wet Cupping removes the toxins that is gathered at the surface of the skin by percutaneous capillary blood filtration. Many certified cupping therapists have noticed that if Wet Cupping is made on a dark purple-black mark, the mark changes color to a lighter color after wet cupping. The color of the red blood cells removed is usually dark-red (almost black); this demonstrate heavy stagnation. The less oxygen the red blood cell has the darker it gets. The heavy stagnation in Traditional Chinese Medicine refers to poor blood circulation in Modern Medicine.
Source:
Hussam Baghdadi and al, Ameliorating Role Exerted by Al-Hijamah in Autoimmune Diseases: Effect on Serum Autoantibodies and Inflammatory Mediators, International Journal of Health Sciences, PubMed PMC4538900 PMID: 26309442
